Human infections caused by the presence of parasites are more common than people think. They can cause serious health complications in both adults and children. There are different types of infections depending on their size and whether there are parasites in a person's blood or on the surface of the body.
Typical symptoms of parasitic infection in the human body
The human body can contain microparasites (malaria) that are only visible under a microscope.
The next group are macroparasites - round and flat worms (nematodes, tapeworms, etc. ) that can often grow to enormous sizes in the body of an infected person.
The presence of parasites in the body is not limited to the intestines, but often affects the lungs, liver, muscles, brain, blood, skin, and even eyes.

The symptoms of the presence of parasites in the human body depend on the type of parasite itself and its toxic waste:
- chronic diarrhea from poor food intake;
- chronic constipation, gas and gas (especially after eating) or other digestive problems including heartburn, abdominal pain and cramps, mucus or blood in the stool, bowel problems, etc;
- puffy eyes and dark circles;
- Fever;
- Pancreatitis;
- Nausea, loss of energy, lethargy, and depression;
- Chills, weakness.
Parasites and skin
The main symptoms of skin parasite infestation are itching. Inflammation of the tissues increases the number of white blood cells that protect the body.
This reaction often causes skin irritation. The person can even develop food allergies.
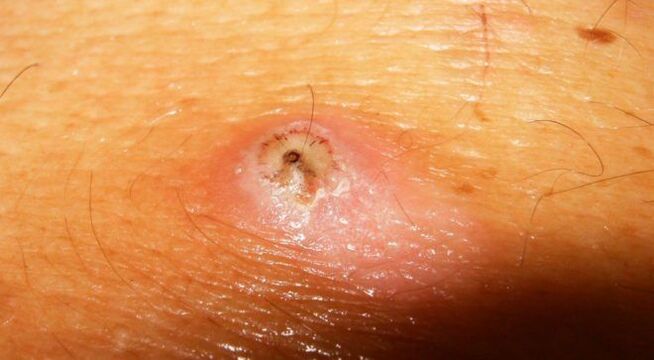
Parasites release toxins and the skin, the largest organ, tries to get rid of them. As a result, various skin problems arise.
Signs of a parasite infestation are:
- dry skin and hair;
- Hair loss;
- Allergies and allergic reactions to food;
- Itching of the nose, skin, or anus;
- Eczema, stomatitis;
- Swelling;
- a feeling of "crawling under the skin";
- Jaundice.
Parasites and the nervous system
Toxins excreted by parasites in humans can affect the central nervous system. Uncertainty and nervousness are often caused precisely by the presence of undesirable organisms in our body.
Signs of parasites in the human body related to the central nervous system:
- rapid and frequent mood swings;
- Anger and irritability;
- Nervousness;
- Depression;
- Forgetfulness and disorganized thinking;
- Fear;
- Fear;
- Slowing down of reflexes;
- Violation of attention.
An infection with parasites poisons the body. The body responds to them even when resting, because at night the manifestations of parasitic infections are most expressive.
Infected people often wake up at night, especially between 2: 00 am and 3: 00 am, when the liver is trying to remove toxins from the body.

This causes the following signs of the presence of parasites in the human body:
- Insomnia and sleep disorders;
- Grinding of teeth in sleep;
- Night sweats and increased salivation.
Often times, signs of the presence of parasites in the body go undiagnosed. "Pests" can live unnoticed in their host's body for a long time and consume the main nutrients obtained from food.
Often, parasites in the body cause a person to eat a lot. However, the infected person cannot gain weight.
Other symptoms of a body infection
Parasites can move around almost any soft tissue, including joints and muscles, where they form cysts and inflammation. These symptoms of parasites in the body are often mistakenly called arthritis or muscle pain.
Parasite toxins often also accumulate in joints and muscles and form muscle cramps and pain, sore joints, stomach, chest, rheumatic pain and an increased heart rate. The signs that appear depend on the system or organ affected.
Parasites are also often responsible for problems related to the urinary and excretory systems. After inhalation, their larvae "migrate" through the airways and cause the following symptoms:
- acute bronchitis;
- Asthma;
- Lung infection;
- To cough;
- Feeling of a foreign body in the throat;
- Difficulties swallowing;
- Bad breath and many others.

The symptoms of parasites in the human body can be very atypical signs, and some types of helminths are very difficult to identify. This is particularly due to the complex diagnosis: it is often necessary to take 3-6 fecal samples to avoid false results. In practice, however, only a negative conclusion is sufficient for the patient's rejection.
Of course, parasites do not hide behind all diseases, but they are often involved in the appearance of some of them. For example, roundworms in the stomach and gastrointestinal tract are manifested by gas and flatulence. Many of these can lead to intestinal blockages and constipation. Ascaris eggs can be swallowed with unwashed vegetables.
Pinworms in the body often cause nausea and diarrhea, they easily penetrate through the intestinal wall into the vascular system, can lead to:
- Hemorrhoids;
- Dismissal in women;
- Inflammation of the bladder;
- Blockage of the biliary tract.
Parasitic infections are often the cause of health problems such as tissue damage (as a result, weakened areas are more easily attacked by viruses and bacteria).
Dizziness and parasites
In the presence of parasites in the human body, symptoms and treatment are closely related. This applies to dizziness, for example. Even our ancestors noticed the connection between leeches and vertigo. All leeches (there are several types of them) reduce metabolism, clog the biliary tract, worsen liver function, and increase cholesterol levels.
Even the largest human parasite, the broad tapeworm, is relatively common. Infections are more common in fishing areas. The source is freshwater fish - pickled or smoked.

Dog and cat tapeworms are no exception, although they are not common in humans.
What can parasites do in the body?
They are able to provoke the development of a number of serious diseases; However, their role in causing such diseases is often overlooked.
- Parkinson's disease can be caused by a combination of several major parasites: Trichomonas vaginalis (Trichomonada vaginalis) with blood that has entered the brain, Treponema pallidum, often congenital, Nocardia (Nocardia asteroids), Echinococcus tapeworm, and other parasites.
- Parasite larvae migrate to the larynx and throat, easily accumulate in the thyroid gland and cause an autoimmune process (which is characteristic of multiple sclerosis). Multiple sclerosis is caused by dysentery (Entamoeba histolytica), Echinococcus (Echinococcus multilocularis), Borrelia, sometimes gonococci or meningococci, etc.
- Similar is the case with ankylosing spondylitis, often caused by echinococci and tapeworms that have invaded the spinal canal and depressing peripheral nerves.
- Epilepsy and dizziness. The cause can be large parasites (Tenia, tapeworm, Echinococcus tapeworm) either in the cerebellum or in the inner ear. Bacterial contamination is common.
The cysts of some parasites have a multilayered protective covering that makes them practically indestructible. A living larva can survive for up to 30 years (Trichinella). Various lumps under the skin can form worms, trichinae, echinococcus tapeworms.
How to remove parasites from the body
To remove parasites from the human body, it is first important to cleanse the entire digestive system. A clean, muscular colon is not a good place for intestinal parasites.
Step 1. Medicinal herbs play an important role in colon cleansing. The most effective are the following:
- Chamomile;
- Tansy;
- Yarrow;
- Oak bark;
- immortelle;
- Mugwort;
- Sea buckthorn bark.
Consuming onions and garlic is a good method. Pumpkin seeds can also treat parasitic infections.

If you can not solve the problem on your own, then you need to contact a specialist who will prescribe anthelmintics.
Important! During treatment, all family members and animals living in the same house must take a therapeutic course to avoid re-infection.
Step 2. Increasing your fiber intake speeds up the time it takes undigested food particles to avoid sedimentation. This reduces the quality of the soil for parasite colonization.
Step 3. Prevention of vitamin deficiencies. Adequate intake of vitamins, minerals, and nutrients is important to fight the parasitic infection.
Step 4. Determining the source of infection and preventing the infection:
- It is important to avoid contact with known sources of infection such as rodent feces, cat feces, and contact with dogs.
- You must be careful when drinking and / or swimming in water of which the quality is unknown.
- To prevent the bites of blood-sucking insects, which can transmit parasites, you need to wear protective clothing.
- Before eating, you should wash all fruits and vegetables in clean water. This also helps prevent infection.
- Water from potentially contaminated sources should not be used to water vegetables.
Children are particularly susceptible to parasitic infestation, and worms are often present in large quantities in children's organisms. Teaching them good hygiene is therefore imperative - washing hands after using the toilet, playing outside, and before eating.
Precautions
Infection can occur through underwear in the same laundry basket, bed linen, towel, household items like toys, cutlery, glasses, and of course, animals (parasites lay invisible eggs on their fur).
It is important to wash bed and underwear frequently in water at a temperature of at least 60 ° C, as well as all clothing that comes into contact with intimate parts of the body. During deworming, these items should be washed daily and separately from other clothing.
It is also recommended to sleep in your underpants to avoid involuntary scratching of the anus during the night when the parasites are most active and lay eggs.
Do not leave pets on your bed, couch, pillows, or blankets.
Sinks and toilets often need to be cleaned with alcohol because many parasitic eggs are resistant to the pH of detergents and soaps.